
Healthy eating should be a part of your plan from the start. Eating a balanced diet and one rich in healthy foods can help improve pregnancy outcomes and decrease the risk of complications with your pregnancy. Your provider may have individualized recommendations based on your needs.
- Gain an appropriate amount of weight during your pregnancy
- Grow a baby appropriately sized for your body and pelvis
- Minimize nausea and dizziness by keeping your blood sugar at an even level
- Expand your blood volume to allow optimal circulation for you and your baby
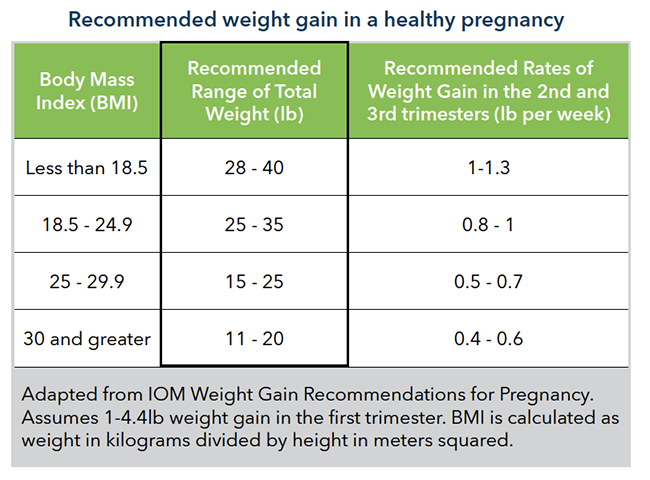
- Calculate your BMI using the CDC BMI Calculator
Eating Right and Getting Plenty of Fluids During Pregnancy Each Day
- High in protein
- Low in fat
- Low in sugar
- Contains calcium and vitamin D
- Contains iron (prevents anemia)
- Plenty of water (at least a quart a day)
- Folic acid (reduces the risk of neural tube defects in baby)
Your Diet Should Include:
- Whole grains foods (2-4 servings per day): whole grain bread, cereal, brown/wild rice
- Vegetables (3-4 servings per day): lettuce, spinach, peppers, cucumbers, carrots, broccoli,
- Fruits (3-4 servings per day): apples, bananas, pears, peaches, melon, prunes, mangoes tomatoes
- Milk, yogurt, cheese (2-4 servings per day): milk (skim or 1%), yogurt and cheese (fat free or low fat)
- Meat, poultry, fish, beans, nuts (2-4 servings per day): fish, eggs, chicken, beans
- Fats and oils (limited quantities): in cooking ingredients
- If you follow a special diet such as vegetarian, vegan, lactose-free, or gluten-free, you should talk with your provider or care team about healthy food choices to ensure proper nutrition for you and your baby. Dieting to lose weight is not recommended during pregnancy.
Recommended Supplements
- Prenatal vitamin with at least 400 - 800 mcg of folic acid.
- Fish Oil (DHA): 200-300 mg per day. This is often available in combined prenatal vitamins.
Foods to keep to a minimum
- Caffeine: No more than 1 - 8 oz cup or 200 mg daily of coffee
- Sugary foods: soda, juice, cookies, cakes, ice cream
- White Foods: white bread, white rice, potatoes, pasta
- Junk Foods: chips, fries, fried foods
Not Recommended in Pregnancy
- Alcohol
- Nicotine
- Marijuana
- Illicit drugs
If you are currently using any of these, please discuss ways to decrease or stop use with your provider
Avoid:
- Foods that may carry listeria or toxoplasmosis (things that can harm the pregnancy).
- Unpasteurized milk/soft cheeses, any unpasteurized beverages like coldpress juices, milk, and certain organic juices
- Deli meats (unless prepackaged or heated prior to eating)
- Smoked fish
- Raw or undercooked meats (all meat should be cooked to above medium temperature)
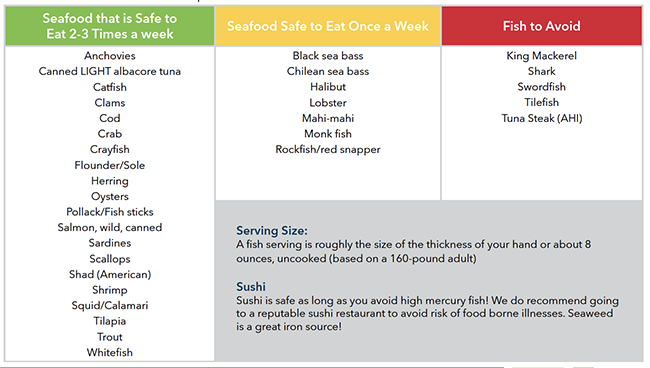
Fish and Seafood
We recommend eating seafood 2 to 3 times per week. Seafood is an excellent protein source and contains omega-3 fatty acids, which help with your baby’s neurological development and lowers your risk of heart disease. However some seafood is high in mercury, which can pose a risk to brain development in fetuses.
Exercise
Exercise is generally safe in pregnancy.
Exercise everyday: for at least 30 minutes. We want to encourage you, as much as possible to stay active
Excellent options include:
- Any routine exercise you were doing prior to pregnancy
- Brisk walking in fresh air: ideal for building the strong legs you will need for labor
- Swimming, elliptical, jogging, stationary biking
- Prenatal yoga
- Light weights (5-10 lb. hand-held weights) - will help you maintain appropriate muscle mass and strength in pregnancy
When You Exercise
Drink lots of water, pay attention to your body and how you feel. Stop your activity and call your provider or care team if you have any of the following:
- Vaginal bleeding
- Dizziness
- Trouble breathing
- Headache
- Chest pain
- Muscle weakness
- Pain or swelling in your lower legs
- Contractions
- Leaking amniotic fluid
- Your baby stops moving
Is Physical Activity Safe For All Pregnant People?
Not everyone should exercise during pregnancy. Your provider will discuss avoiding exercise if you have:
- Heart problems that affect blood flow
- Preterm labor – preterm labor is labor that happens too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy
- An insufficient cervix – this is a cervix that opens and/or shortens too early, before the baby is full term
- Lung disease
- Vaginal bleeding during the second or third trimester (from 4 months of pregnancy on) that doesn’t go away
- Ruptured membranes (when your water breaks)
- Preeclampsia – this is a condition that can happen after the 20th week of pregnancy or right after pregnancy. It’s when a person has high blood pressure and signs that some of their organs, like kidneys and liver may not be working properly.
- Placenta previa – this is when the placenta sits low in the uterus and covers all or part of, the cervix.
Things to Avoid
- Any activity that may hurt you or cause you to fall, such as horseback riding, downhill skiing, gymnastics, surfing, or bike riding
- Any activity or sport in which you may get hit in the belly, such as ice hockey, kickboxing, soccer, diving, basketball, or baseball
- Any exercise that makes you lie flat on your back, like sit-ups, after the 3rd month of pregnancy. Lying on your back can limit the flow of blood to your baby
- Scuba diving
- Exercise at high altitudes, (more than 6,000 feet)
- Activities or exercise in heated environments or hot, humid days to avoid overheating
- Stay out of saunas, hot tubs, and steam rooms
